Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
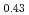 Am
Am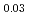 U
U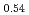 )O
)O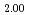
Nakamichi, Shinya; Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 96(1), p.191 - 192, 2007/06
JAEA has developed plutonium and uranium mixed oxide (MOX) containing 20-32%Pu content as a fuel of the fast breeder reactor. During irradiation, large temperature gradient in radial direction of a fuel pellet causes redistribution of Pu and U, and the Pu content increases to about 43% at the pellet center. The maximum temperature of the fuel pellet during irradiation is limited within the design criterion to prevent fuel melting. So, it is important to evaluate melting points of MOX containing 43%Pu. In this work, it is confirmed that the MOX with 43%Pu content is not melted by heat treatment just below the melting point which was determined by thermal arrest technique using Re inner capsule. The MOX specimen with 43%Pu content was heated at 2978K for 40s using Re inner capsule. Optical micrograph and XRD results show the specimen was heated at the temperature less than solidus temperature. So it was confirmed that (Pu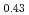 Am
Am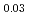 U
U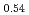 )O
)O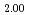 was solid phase at 2978K
was solid phase at 2978K 20K.
20K.
Kato, Masato; Morimoto, Kyoichi; Sugata, Hiromasa*; Konashi, Kenji*; Kashimura, Motoaki; Abe, Tomoyuki
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 96(1), p.193 - 194, 2007/06
Melting point of a nuclear fuel is one of the important physical properties for its development, because it limits maximum temperature of the fuel during operation. A rhenium inner capsule was used to prevent the reaction with capsule for measuring melting points of MOX. In this work melting points of MOX with 40% and 46%Pu were investigated as a function of an O/M ratio using Re inner, and the effect of the O/M ratio on the melting points was evaluated. The solidus and liquidus temperatures in (Pu U
U )O
)O and (Pu
and (Pu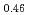 U
U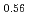 )O
)O were measured by thermal arrest method. It was observed that the melting points in the both samples increased with a decrease of the O/M from 2.00, and their data were 50-100K higher than existing data measured in previous works which were measured with W capsule.
were measured by thermal arrest method. It was observed that the melting points in the both samples increased with a decrease of the O/M from 2.00, and their data were 50-100K higher than existing data measured in previous works which were measured with W capsule.
Iwamura, Takamichi
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 96(1), p.743 - 744, 2007/06
The Feasibility Study on commercialized fast reactor cycle systems was carried out to elucidate prominent fast reactor cycle systems that would respond to various needs of society in the future. As the result of phase-II, the combination of the sodium-cooled fast reactor with oxide fuel, the advanced aqueous reprocessing and the simplified pelletizing fuel fabrication was selected as the most promising concept. In March 2006, CSTP of the cabinet office selected fast reactor cycle technology as one of key technologies of national importance. After this, the action plans on nuclear technology development completed by MEXT and METI stated a start-up of a demonstration fast reactor by 2025 and deployment of a commercial fast reactor cycle before 2050. "Fast Reactor Cycle Technology Development Project" (FaCT Project) was launched to realize these targets. In this project, conceptual design study and innovative technologies development will be carried out by 2015.
Hayashi, Takao; Sakurai, Shinji; Masaki, Kei; Tamai, Hiroshi; Yoshida, Kiyoshi; Matsukawa, Makoto
Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, 96(1), P. 783, 2007/06
JT-60SA equipped with fully superconducting magnets is now being designed as a combined project of the Japanese national project toward DEMO reactor and a satellite tokamak project for ITER in a Broader approach with Japan and EU collaboration. Because the expected dose rate at the vacuum vessel (VV) may exceed 1 mSv/hr after 10 years operation and three month cooling, the human access inside the VV is prohibited. This indicates a remote handling (RH) system is necessary for the maintenance and repair of in-vessel components. This study described the RH system of JT-60SA to exchange or repair the in-vessel components such as first wall tiles and divertor modules. First wall armor tiles fully cover the plasma-side surface of the VV to protect from the plasma. Bolted armor tiles, made by graphite or ferritic steel, on a heat-sink can be replaced by LWM in the VV.
Ono, Kiyoshi; Mukaida, Kyoko; Shiotani, Hiroki; Hirao, Kazunori
no journal, ,
GIF Economic Modeling Working Group (EMWG) is developing the G4-ECONS code for economic study of the generation IV nuclear systems. In this paper, we would like to introduce the outline of the total system cost analysis for Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) sodium cooled fast reactor (JSFR) and its fuel cycle, as an application sample of the G4-ECONS bottom-up approach, and the results of the comparison of it with JAEA original cost estimation using our own calculation model (FCC-EX code). The result of comparison between the electricity generation cost calculated by G4-ECONS code and FCC-EX code demonstrated the validity of calculation function of the G4-ECONS code.
Shiozawa, Shusaku; Hino, Ryutaro; Ogawa, Masuro
no journal, ,
A High-Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR), which is a graphite moderated, helium cooled reactor, is particularly attractive due to capability of producing high temperature helium gas and its inherent safety characteristics. Especially the hydrogen production using HTGR heat is expected to be one of the most promising applications to solve the current environmental issues of CO emission. With this understanding JAEA has proceeded with the development studies of the thermochemical water splitting IS process as well as HTGR reactor technology in the HTTR Project. In the invited panel session, the Japan's policy for HTGR and nuclear hydrogen is given as an introduction, followed by summary of nuclear hydrogen development works in Japan. And the HTTR Project which is underway at JAEA is explained, focusing on the achievements concerning the IS process technology development and future plan. Finally, personal future perspective will be introduced, followed by concluding remarks.
emission. With this understanding JAEA has proceeded with the development studies of the thermochemical water splitting IS process as well as HTGR reactor technology in the HTTR Project. In the invited panel session, the Japan's policy for HTGR and nuclear hydrogen is given as an introduction, followed by summary of nuclear hydrogen development works in Japan. And the HTTR Project which is underway at JAEA is explained, focusing on the achievements concerning the IS process technology development and future plan. Finally, personal future perspective will be introduced, followed by concluding remarks.